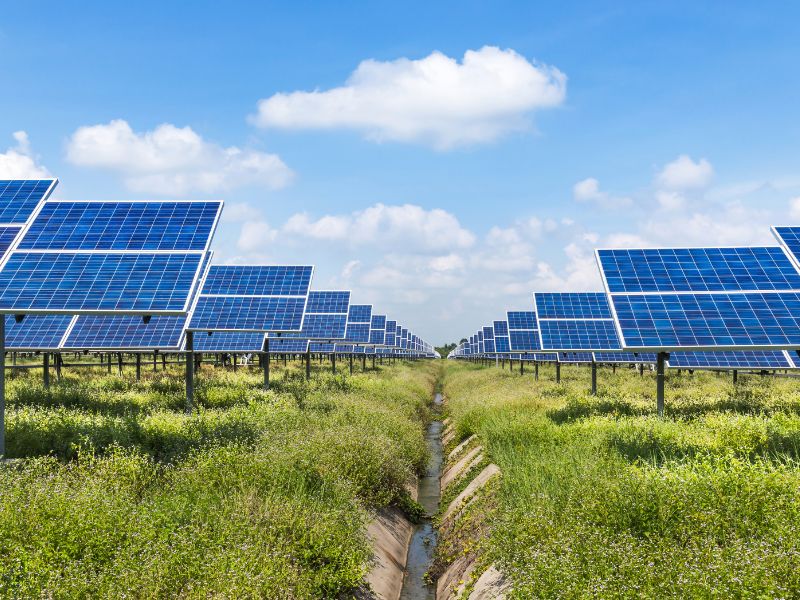
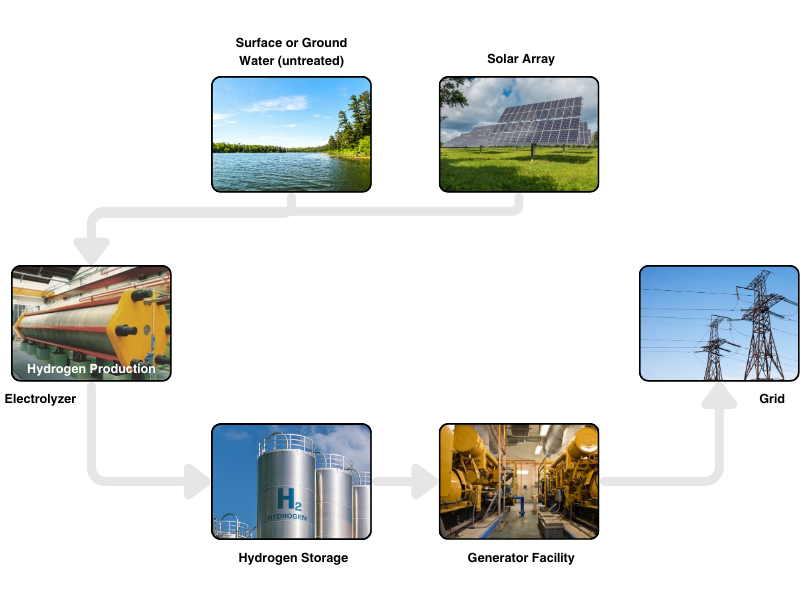
Solar Array
The solar array is housed on a dual axis tracking system that provides approximately 45% more power than fixed tilt installations as previously stated. The array on each tracker can vary from 12 to 42 panels. Maximum power output per tracker is 21 Kw.
Untreated Water
Water for the production of hydrogen and potable water can be from any source such as pond, stream, sea, well and even waste. The primary water is pumped to the plant and stored for processing of both the potable and distilled water.
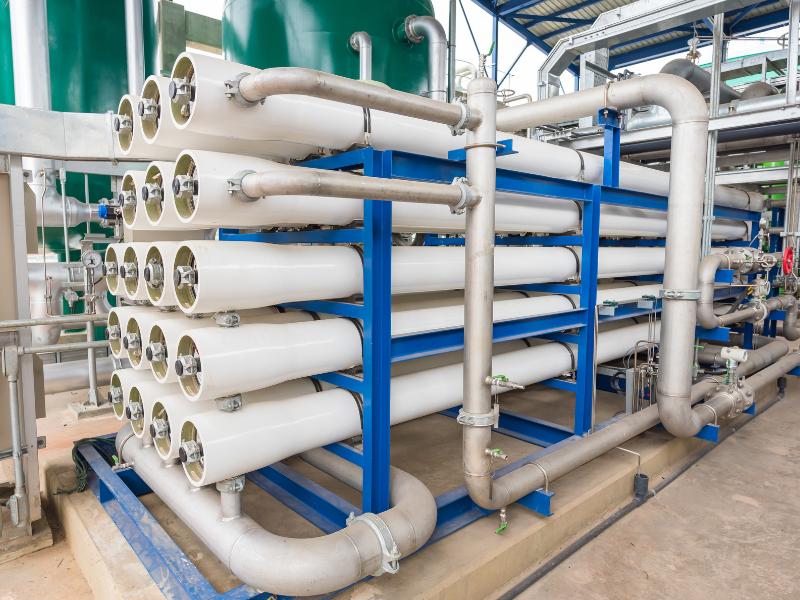
Reverse Osmosis Process
The Hydrogen Cycle uses the reverse osmosis process (RO) to purify water before its use in the electrolyzers to produce the hydrogen. The RO process uses five stages of filtering to remove all the suspended solids in the water.
Electrolyzers
There are two methods of electrolysis for production of the hydrogen. PEM electrolysis is used primarily in small plants and alkaline electrolysis which is faster and less expensive is used in larger installations.
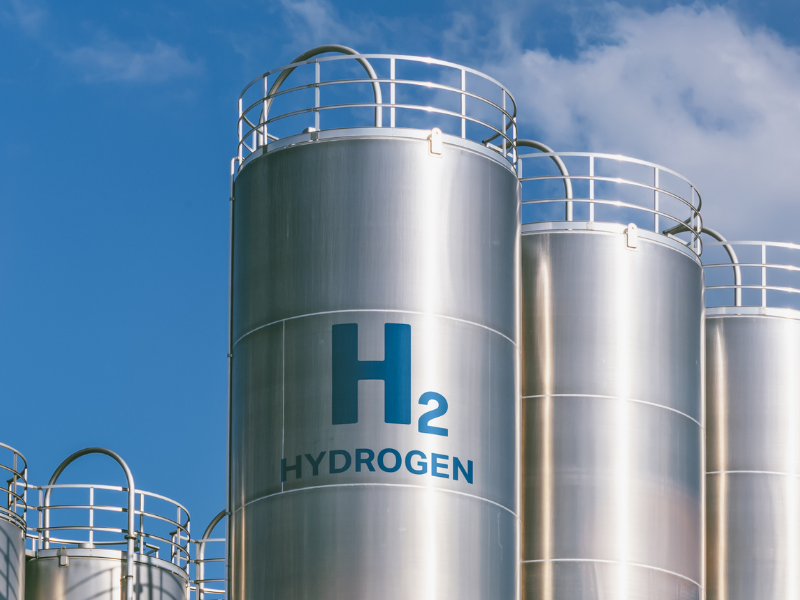
Hydrogen Storage
The hydrogen leaves the electrolyzer at 400 to 500 psi and flows into a large distribution tank. When the distribution tank is nearing capacity, the hydrogen is pumped to smaller primary vessels and pressurized to 10,000 psi for storage.
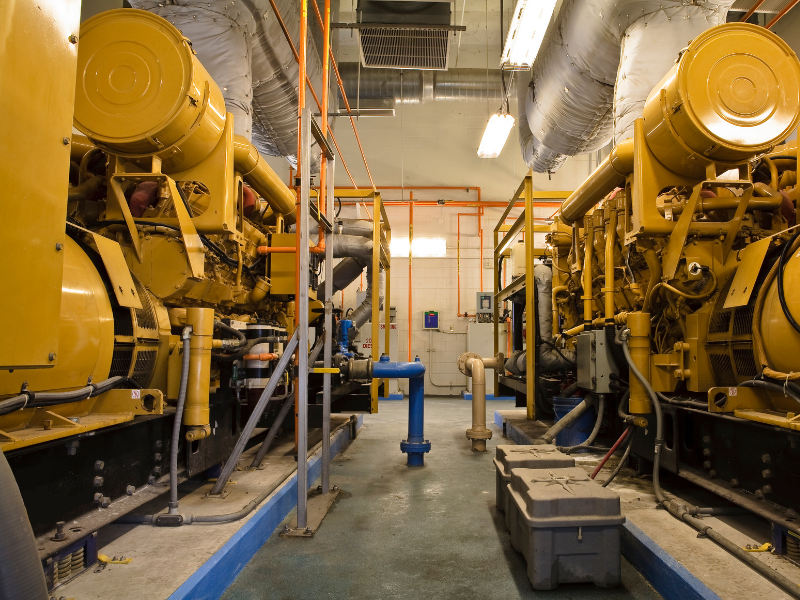
Generators
Hydrogen is a unique fuel. When burned, it produces no carbon dioxide. The exhaust from hydrogen combustion is water vapor. From each of the internal combustion engines or gas turbines, the exhaust is run through a condenser capturing and cooling the water vapor which changes its state back to water to be used again and producing hydrogen, thus The Hydrogen Cycle.
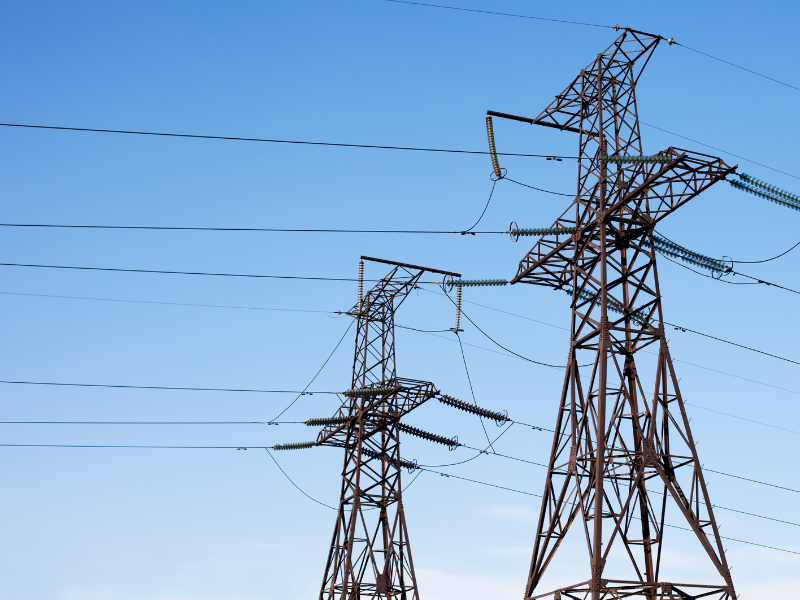
Energy Grid
Power from both the solar array and the hydrogen generators is distributed to the community or the grid to sustain 24-hour power.